When the lights flicker and die, a comfortable home transforms into a cold, dark environment in minutes. Although the European power grid is historically reliable, it currently faces unprecedented strain from extreme weather, aging infrastructure, and the green energy transition. These outages threaten far more than minor inconveniences; they sever essential heating, water, and communication lines, making safety the immediate priority.
However, strategic preparation can downgrade a blackout from a crisis to a manageable inconvenience. This guide serves as a practical playbook for building resilience, ensuring that through risk understanding and resource assembly, your household remains safe, warm, and self-sufficient when the grid goes down.
Understanding Blackouts in Europe: Risks and Realities
Not all power cuts are the same, and the response required depends heavily on the cause and expected duration of the interruption.
What Are the Different Types of Power Threats?
Grid disruptions fall into two primary categories: controlled and uncontrolled. Rolling blackouts are planned events implemented by grid operators to prevent total system collapse, typically lasting 2 to 4 hours. These are usually announced in advance when demand exceeds supply.
Unplanned grid failures are chaotic and unpredictable. These result from technical faults, cyber threats, or severe weather events like storms and heatwaves.
How Long Can These Outages Last?
Most localized faults are resolved within a few hours. Repair crews can typically fix a downed line or a blown transformer relatively quickly. However, systemic issues or severe storm damage present a different challenge.
Regional events can persist for 24 to 72 hours. A major European grid outage caused by cascading failures across borders could take days to stabilize. Therefore, household preparedness plans must cover a minimum of three days of total self-sufficiency.
Who Is Most at Risk?
Vulnerability during a blackout depends on health and housing type. Elderly residents are more susceptible to hypothermia during winter outages. Individuals relying on electrically powered medical equipment, such as oxygen concentrators or CPAP machines, face immediate life-threatening risks.
Residents in high-rise apartments face unique challenges. When power fails, elevators stop, and water pumps often cease functioning, cutting off the water supply to upper floors. Identifying these vulnerabilities in advance allows for specific contingency planning.
Who Should You Contact During a Blackout in Europe?
In most European countries, you should contact your local Distribution System Operator (DSO)—the company that owns the physical grid in your specific region—rather than your energy supplier (the company that bills you).
Below is the contact protocol for each requested country:
|
Country |
Primary Contact / Number |
Details |
|
Netherlands |
0800-9009 |
This is the National Outage Number (Nationaal Storingsnummer). It is free, available 24/7, and automatically connects you to your regional grid operator (e.g., Liander, Enexis, or Stedin). |
|
Sweden |
Local DSO |
You must contact the company that owns the grid in your area. Major operators include Vattenfall (020-82 58 58) and Ellevio (0771-53 53 00). For general crisis info, call the national number 113 13. |
|
Finland |
Local DSO |
Contact your local distribution company (e.g., Caruna at 0800 195 011). You can view a real-time nationwide outage map at https://sahkokatkokartta.fi/. |
|
Italy |
Local Distributor |
Most of Italy is served by E-Distribuzione; you can report outages via their dedicated online portal or app. While Terna manages the high-voltage national grid, they do not handle individual household outages. |
|
Belgium |
Regional DSO |
Contact varies by region: Fluvius in Flanders, ORES or RESA in Wallonia, and Sibelga (02 274 40 66) in Brussels. You can find your specific operator via the Energie-Info website. |
|
Norway |
Local Grid Co. |
Contact your local nettselskap (grid company). Major providers like Elvia or BKK provide live maps and SMS alerts for their specific service areas. |
|
Switzerland |
Local Utility |
Power is managed by local or cantonal utilities (e.g., EWZ in Zurich, SIG in Geneva, or BKW in Bern). You should call the emergency number listed on your local utility bill. |
Backup Power Solutions For Grid Outages
Relying solely on the grid is no longer a guaranteed strategy. Integrating backup power solutions into your home setup provides a safety net for critical devices. While exploring power backup solutions for grid outages reveals various technologies, the market generally offers solutions ranging from pocket-sized chargers to whole-home systems.

Small Scale: Keeping Communication Alive
For minimal needs, keeping communication lines open is the priority.
- Power Banks: Typically 10,000mAh to 20,000mAh. Essential for recharging smartphones 2-3 times to make emergency calls and check local news updates.
- Solar Chargers: Small, foldable panels with USB outputs. Useful for directly topping up small devices during sunny periods, though charging speeds are slow compared to wall outlets.
Medium to Large Scale: Home Backup & Medical Needs
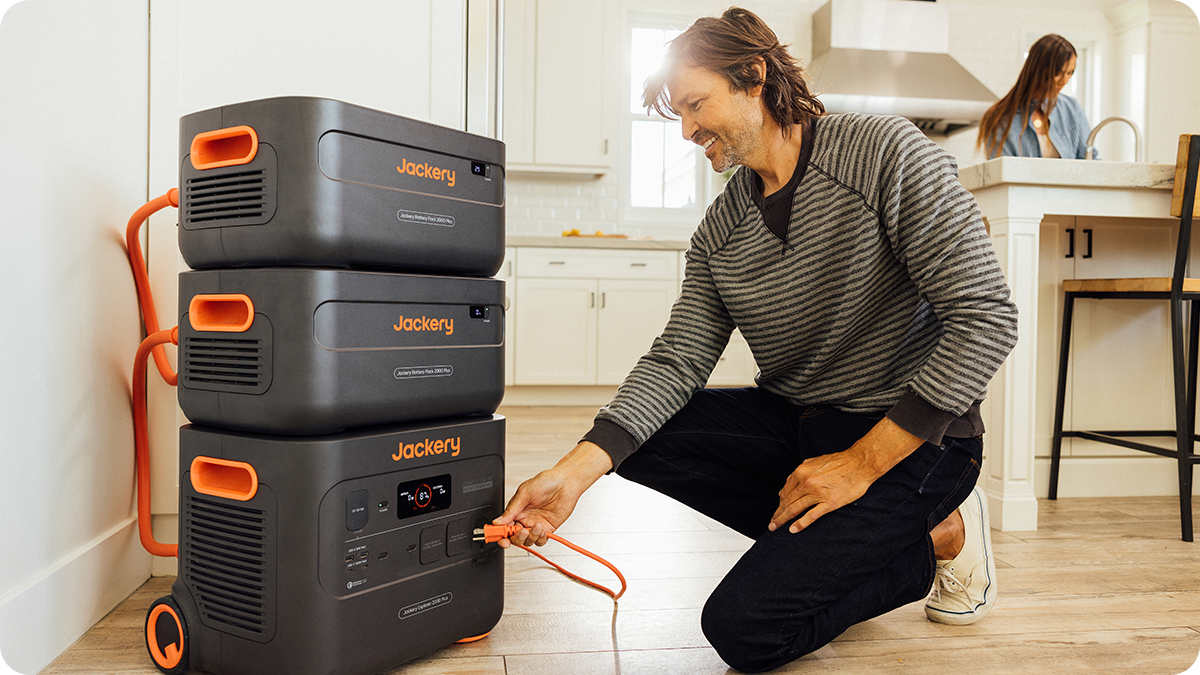
Portable Power Stations (PPS) have become the standard for modern emergency preparedness. These battery-powered inverters are silent, emit no fumes, and are safe for indoor use, unlike gas generators.
- Capacity: 2042Wh.
- Battery Chemistry: LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) offers superior safety and a lifespan of 4000 cycles to 70% capacity.
- Fast Charging: Jackery Explorer 2000 v2 recharges from 0-100% via wall outlet in 1.7 hours (or 1.33 hours with Emergency Super Charge), allowing for rapid top-ups if grid power returns briefly.
- UPS Function: Features a <20ms switchover time.
- Use Case: The unit is capable of powering a household refrigerator (15-520W) for 3.2 to 72 hours or keeping medical devices running through the night.
The UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) feature is particularly critical for medical equipment and computers. It ensures that when the mains power cuts, the battery takes over instantly, preventing data loss or equipment shutoff. Learning how to build your home power backup system correctly ensures these features function when needed most.
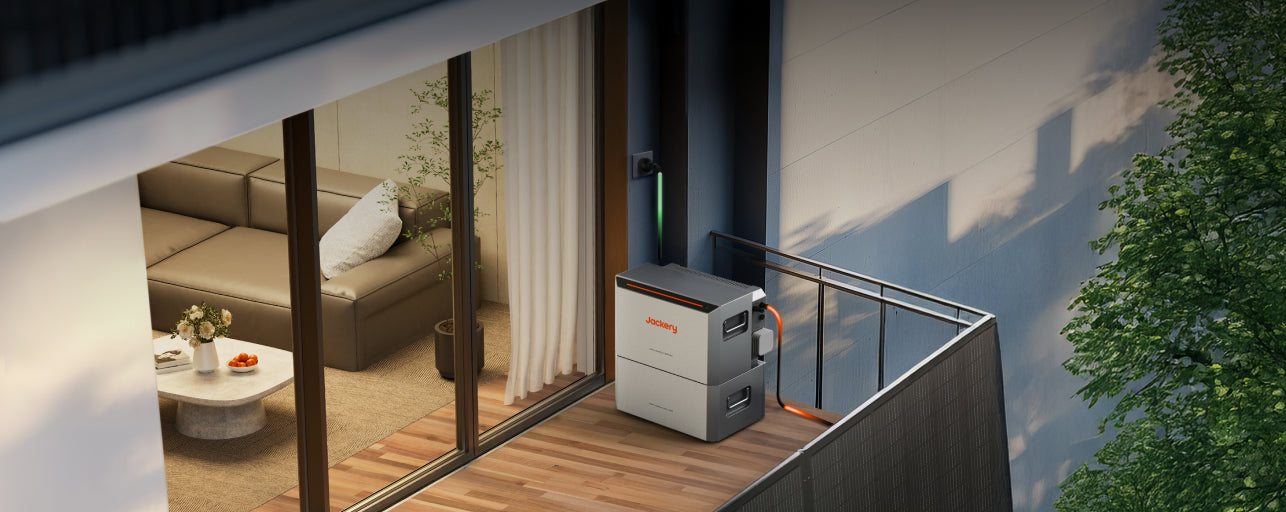
Heavy Duty: Extended Outages
For outages in Europe that last several days, or for households with higher energy demands, larger capacity systems are required.
- Capacity: 3072Wh battery capacity.
- Output: 3600W power output (Surge 7200W).
- Use Case: Jackery Explorer 3000 v2 is sufficient to run high-load devices such as electric kettles (850W), electric ovens (960W), and power tools during extended disruptions.
Solar Integration Pairing these batteries with portable solar panels (e.g., SolarSaga 200W) transforms the unit into a solar generator. This allows for off-grid recharging, theoretically extending runtime indefinitely as long as there is sunlight. This independence is vital when fuel for traditional generators is unavailable.
Actions During a Blackout: The First 24 Hours
The moment the power goes out, your actions determine how comfortable and safe the next few days will be. Panic leads to poor decisions; a systematic approach ensures safety.
|
Priority Area |
Action Step |
Procedure & Rationale |
|
Electronics Protection |
Unplug Sensitive Devices |
Immediately disconnect TVs, computers, and microwaves. This protects hardware from damaging voltage surges that often occur when power is suddenly restored. |
|
Lighting Strategy |
Manage Switches |
Leave exactly one light switch ON to signal when power returns. Keep all others OFF to prevent a massive, simultaneous load on the home's wiring. |
|
Thermal Comfort |
Isolate Heat |
In winter, close doors to unused rooms to create a smaller "warm zone." Use towels or draft stoppers to seal gaps under doors and prevent heat escape. |
|
Food Preservation |
Minimize Access |
Keep refrigerator and freezer doors shut. An unopened fridge stays cold for ~4 hours; a full freezer maintains temperature for ~48 hours. |
|
Power Management |
"Duty Cycle" Cooling |
If using a portable power station, run the fridge for 1 hour on, then 3 hours off. This strategic cycling maintains food safety while significantly extending backup battery life. |
|
Mobile Battery |
Activate Power Saving |
Switch phones to "Low Power" or "Airplane Mode" when not in use. This stops background apps from draining the battery while searching for weak signals. |
|
Information |
Use Analog Radio |
Rely on a battery-powered radio for official updates. Avoid scrolling social media, as it drains phone battery andis often less accurate than local broadcasters. |
Post-Blackout Recovery and Lessons Learned
When the lights finally return, the emergency is not immediately over. The grid may be unstable for the first hour as millions of devices reconnect simultaneously.
How Do You Safely Reconnect?
Wait 10 to 15 minutes after power returns before plugging in major appliances. This patience helps stabilize the grid load and protects your expensive equipment from residual voltage fluctuations.
How Do You Check Your Food Supply?
Inspect your food supplies critically. If the refrigerator temperature rose above 4°C for more than two hours, perishables like meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and leftovers are likely unsafe. The cost of replacing food is far lower than the cost of food poisoning. When in doubt, throw it out.
How Do You Restock and Review Your Plan?
Recovery is the best time to prepare for the next event. Replenish water stocks and non-perishable food immediately, as stores may be crowded later. Recharge your power stations and power banks to 100% capacity.
Sit down with your family to discuss what worked and what failed. Did you have enough light? Was the house too cold? Did the backup battery last as long as expected? Adjust your plan and equipment list based on this real-world test.
Community Resilience
Individual preparedness contributes to broader community security. When you are self-sufficient, emergency services can focus on the most vulnerable.
How Can Neighbors Help Each Other?
Resilience is stronger when shared. Form neighborhood groups to check on elderly or disabled residents during outages. A simple knock on the door to ensure a neighbor has heat or water can save a life.
Future Trends in Europe
Why Is Decentralized Energy Growing?
The trend across Europe is moving toward decentralized energy. Households are increasingly adopting personal energy independence measures. Using solar generators reduces reliance on the central grid, lowering the strain on the system and providing security regardless of the grid's status.
What Is the Status of Grid Modernization?
While governments and utility companies are investing heavily in grid modernization and smart interconnectors, these projects take years. The transition to renewable energy sources introduces variability that the old grid was not designed to handle. Consequently, individual preparedness remains the fastest and most reliable way to ensure household security in the immediate future.
Quick Reference Checklists
Power Priority List
- Medical Devices: CPAP, oxygen concentrators (Critical).
- Communication: Phones, radios (High).
- Refrigeration: Fridge/Freezer (Medium - cycle power).
- Comfort: Lights, fans, entertainment (Low).
Safety Rules
- Never run gas generators indoors or in garages.
- Never leave lit candles unattended.
- Always unplug sensitive electronics when power cuts.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I purify water during an extended outage?
You can use portable water filtration systems or chemical purification tablets. If you have a safe heat source, boiling water for at least one minute is the most effective method.
What are safe heating options without electricity?
Indoor-safe propane heaters (used with proper ventilation) or wood-burning stoves are effective options. Wearing layers of wool or synthetic thermal clothing and using sleeping bags is the safest passive method.
Can my solar panels power my home directly during a blackout?
Most standard roof solar systems shut down during a blackout for safety reasons. You can only power your home if your system is connected to a battery storage system with islanding capabilities.
Are there government programs to assist with preparedness costs?
Many European countries offer grants or subsidies for energy efficiency upgrades, which sometimes include battery storage. Research local or national initiatives specifically targeting renewable energy adoption and emergency resilience.